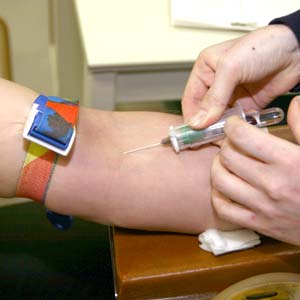
Description of the test
Liver function tests are done by taking a sample of blood from your body and checking the levels of certain enzymes and proteins in your blood.
The liver is our largest internal organ and performs many important functions within the body. By looking at certain enzymes and proteins in the blood produced by the liver, doctors can determine if there are any problems with the liver and how it is working. Blood liver enzyme tests measure the enzymes in the blood. Liver function tests measure how well the liver is working and generally refer to the proteins (e.g., albumin and total protein) in the liver. However, "liver function tests" are often used to refer to both the tests that measure enzymes and the tests that measure proteins.
How often should the test be performed?
Your doctor will decide when and how frequently this test is required.
Why is this test performed?
Having this test means that your doctor wants more information about the health of your liver. This test is often done with routine blood work that is part of a physical exam. Also, if you have hepatitis B or C, a chronic liver condition, or are taking medication that may affect the liver (e.g., some cholesterol-lowering medications), a doctor may order this test.
If the test shows that your liver is not functioning well, your doctor may change the dose of some of your medications or may change your medications.
Your doctor also may want to determine if you have:
- liver damage caused by drinking too much alcohol
- other conditions related to your symptoms
Are there any risks and precautions?
There is very low risk of side effects with this test. The test may have a risk of infection (if the area is not properly sterilized before the sample is taken), bleeding from where the needle was inserted, or bruising around the area where the needle was inserted.
People with bleeding disorders or anyone taking medication that reduces the ability of the blood to clot (e.g., warfarin, ASA, or other anticoagulants) should tell the technician before the samples of blood are taken. These conditions and medications may require special attention when the blood is taken.
What happens during the test?
- A technician or nurse wraps a wide elastic band around your upper arm to help locate the vein.
- Once the vein is located, usually on the inside of your elbow, the area is disinfected using an alcohol swab.
- The technician inserts a needle into a vein and pushes a vial (labelled with your name and other information) onto the needle to collect the blood.
- The elastic band is removed and after the blood is collected, the needle is removed and discarded.
- You will have to hold a small piece of cotton over the area until bleeding stops. A small bandage will be applied to hold the cotton in place.
The whole process only takes a few minutes. The technician wears fresh latex gloves and uses a new, single-use needle for each procedure.
The test is almost painless for most people, although feeling a slight pinch when the needle is inserted is normal. The vials of blood are then sent to a laboratory to be tested.
How should I prepare for this test?
In most cases you do not need to do anything to prepare for this test.
Clothing with no sleeves or loose sleeves is recommended so your upper arm can be exposed.
Tell your doctor or prescriber about all prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have.
Your doctor may ask you not to eat prior to the test because some foods may affect the results. Be sure to follow any specific instructions provided by your doctor or the clinic.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist whether you need to stop taking any of your medications before the test.
What can I expect after the test?
You may have some slight tenderness where the needle was inserted. Keep pressure on the area after the needle is removed to prevent bruising. Follow any instructions provided by the technician.
Results
Your doctor reviews the results from the laboratory. Ask your doctor when your test results should be available.
Results return in the form of a number. Higher-than-average numbers are a possible sign of liver damage. If the results are high for a long period of time, this could mean you have a chronic liver infection (e.g., hepatitis C virus) or chronic liver disease. High liver enzymes may occur for many other reasons, including:
- viral or bacterial infections
- certain medications (e.g., some cholesterol-lowering medications)
- excessive use of alcohol
- joint- and bone-related problems
- certain types of cancer
- diabetes that has been poorly controlled
- gall bladder diseases
To diagnose a specific condition, your doctor may need you to do further tests.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Blood-Liver-Enzymes-Test